In the realm of technological innovation, blockchain stands out as a revolutionary development that has the potential to transform various industries. Originally designed as the underlying technology for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain’s applications have since expanded far beyond digital currencies. This article explores the purpose of blockchain technology, its core principles, and its diverse applications across different sectors.
What Is Blockchain Technology?
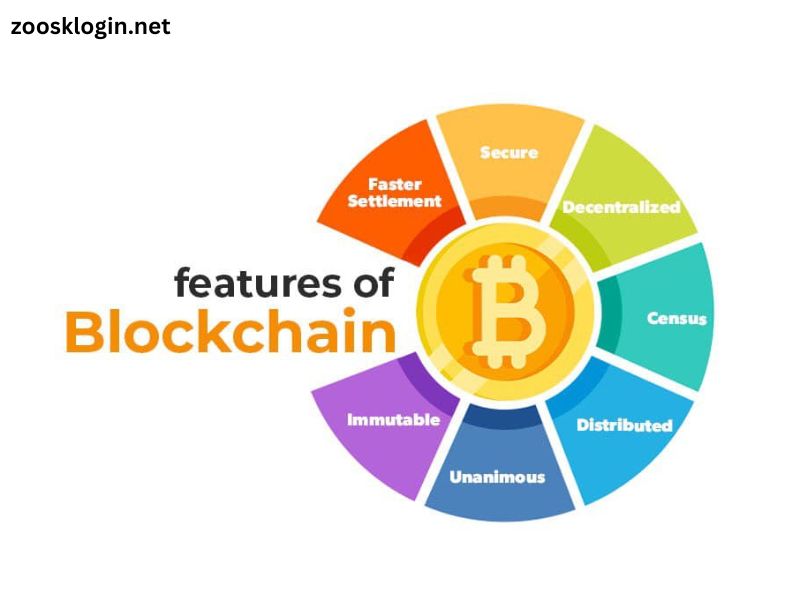
At its core, blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers in a way that ensures the security and transparency of data. Unlike traditional databases that are typically managed by a central authority, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network. Each participant in the network maintains a copy of the ledger, and any changes to the data must be agreed upon by the majority of participants, making it highly resistant to tampering and fraud.
A blockchain consists of a series of blocks, each containing a list of transactions. These blocks are linked together in a chronological order, forming a chain. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, ensuring that the entire chain is immutable and secure. This structure provides a high level of trust and reliability, as altering any block would require changing all subsequent blocks, which is computationally infeasible.
Core Principles of Blockchain Technology
1. Decentralization
One of the fundamental principles of blockchain is decentralization. In a traditional centralized system, a single entity controls the database and its transactions. In contrast, blockchain distributes the control across a network of nodes (computers) that collectively manage the ledger. This decentralization reduces the risk of a single point of failure and enhances the system’s resilience to attacks and malfunctions.
2. Transparency
Blockchain technology promotes transparency by providing a public ledger that is accessible to all participants in the network. Every transaction recorded on the blockchain is visible to all participants, making it easier to track and verify transactions. This transparency helps build trust among users, as they can independently verify the accuracy of the data without relying on a central authority.
3. Immutability
Once data is recorded on a blockchain, it is virtually impossible to alter or delete it. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a secure and unchangeable record of all transactions. This immutability ensures that the data remains accurate and reliable, providing a permanent and verifiable history of all activities on the blockchain.
4. Security
Blockchain technology employs advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data and transactions. Each transaction is encrypted and added to a block, which is then linked to the previous block using a cryptographic hash. This encryption and hashing process ensures that the data is protected from unauthorized access and tampering. Additionally, the decentralized nature of blockchain reduces the risk of a single point of failure, making the system more secure against attacks.
Purpose of Blockchain Technology
1. Cryptocurrencies
The most well-known application of blockchain technology is in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Blockchain provides a secure and transparent way to record and verify digital transactions without the need for a central authority. Cryptocurrencies leverage blockchain to create a decentralized financial system, allowing users to transfer value globally with minimal transaction fees and without intermediaries.
2. Supply Chain Management
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize supply chain management by providing a transparent and traceable record of goods as they move through the supply chain. Each step in the supply chain, from production to delivery, can be recorded on the blockchain, providing real-time visibility and reducing the risk of fraud and errors. This increased transparency helps improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance trust among supply chain participants.
3. Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts are stored and executed on the blockchain, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of disputes. Smart contracts automatically enforce and execute the terms of an agreement when predefined conditions are met, streamlining processes and increasing efficiency in various industries, including finance, real estate, and legal services.
4. Voting Systems
Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent solution for voting systems. Traditional voting methods are often susceptible to fraud, tampering, and inaccuracies. By using blockchain to record and verify votes, election processes can become more secure and transparent. Each vote is recorded as a transaction on the blockchain, creating a permanent and tamper-proof record of the election results. This approach enhances the integrity of the voting process and increases public trust in election outcomes.
5. Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, blockchain technology can improve the management and sharing of medical records. Blockchain provides a secure and interoperable platform for storing and accessing patient data, ensuring that medical records are accurate, up-to-date, and accessible only to authorized individuals. This approach can enhance patient care, streamline administrative processes, and reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
6. Identity Management
Blockchain technology offers a decentralized and secure solution for identity management. Traditional identity systems are often centralized and vulnerable to fraud and data breaches. Blockchain-based identity management allows individuals to have control over their personal information and share it securely with authorized parties. This approach enhances privacy and reduces the risk of identity theft and fraud.
7. Intellectual Property Protection
Blockchain technology can be used to protect intellectual property rights by providing a transparent and immutable record of ownership and usage. Artists, musicians, and other creators can use blockchain to register and track their works, ensuring that their intellectual property is protected and that they receive fair compensation for its use. This approach helps address issues related to copyright infringement and unauthorized distribution.
Challenges and Limitations
While blockchain technology offers numerous benefits, it also faces several challenges and limitations. One of the primary challenges is scalability. As the number of transactions on a blockchain increases, the size of the blockchain grows, which can lead to slower processing times and higher costs. Additionally, the energy consumption associated with blockchain mining and consensus mechanisms can be significant, raising concerns about environmental impact.
Another challenge is regulatory uncertainty. The legal and regulatory framework for blockchain technology is still evolving, and different jurisdictions may have varying requirements and restrictions. This uncertainty can create obstacles for businesses and individuals looking to adopt blockchain solutions.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology has the potential to transform a wide range of industries by providing secure, transparent, and decentralized solutions for various applications. From cryptocurrencies and supply chain management to voting systems and healthcare, blockchain offers innovative ways to improve efficiency, reduce fraud, and enhance trust. However, challenges such as scalability, energy consumption, and regulatory uncertainty must be addressed to fully realize the potential of blockchain technology. As the technology continues to evolve, its impact on various sectors will likely grow, shaping the future of digital transactions and data management.
Understanding the purpose of blockchain technology and its diverse applications is crucial for individuals and businesses looking to leverage its benefits. By embracing blockchain and exploring its potential, we can unlock new opportunities and drive innovation in the digital age.